Is fatty liver a lifestyle disease?
By 𝗡𝗮𝘃𝗮𝗺𝗶 𝗩𝗶𝗷𝗮𝘆𝗮𝗻 𝗣 (Dietitian)
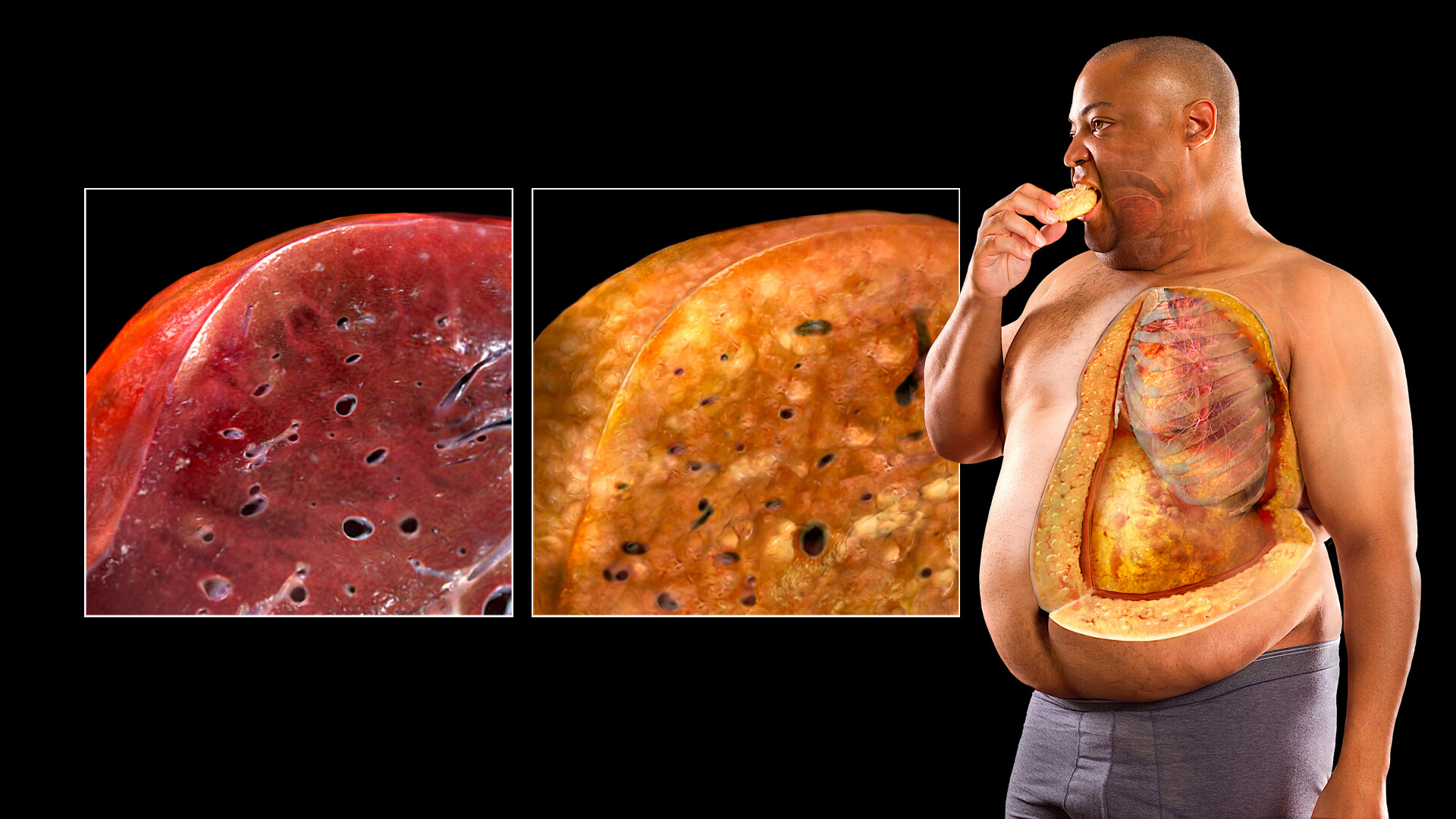
August 9, 2024Fatty liver is a lifestyle disease that is a reflection of unhealthy lifestyle and habits. Unlike previous times, the number of people affected by fatty liver is increasing. Another worrying fact is the increase in the number of young people affected by fatty liver. The role played by the liver in the proper functioning of the body is very important. But fatty liver is a condition in which fat accumulates in the liver due to various reasons. A fatty liver is defined as a fat accumulation of more than 5%. There are two types of fatty liver: alcoholic fatty liver, which is caused by excessive alcohol consumption, and non-alcoholic fatty liver, which is caused by excessive alcohol consumption.
People with lifestyle diseases like diabetes, high blood pressure and cholesterol are more prone to fatty liver.
Also, obesity and excessive alcohol consumption increase the risk of fatty liver. Fatty liver is also seen in some people as a side effect of certain medications and as part of diseases such as Wilson's disease. Most people with fatty liver experience no noticeable symptoms. If not diagnosed and treated at an early stage, it can lead to serious health problems such as liver cirrhosis. Swelling in the legs and abdomen are common symptoms of liver cirrhosis.
Grade 1 fatty liver, also known as simple fatty liver, is the early stage of fatty liver disease. At this stage, there is very little accumulation of fat in the liver cells and the liver does not suffer much damage. However, it is essential to treat this condition immediately because it can progress to more severe stages of fatty liver disease, such as grade 2 or 3.
Grade 1 fatty liver can be controlled through healthy lifestyle changes along with treatment. Grade 1 fatty liver disease is not dangerous if it is in the early stages, as fat accumulation is less than one-third of the total liver. Therefore, studies show that it can be reversed with the help of diet, physical exercise, weight loss and complete abstinence from alcohol. proving
● Work up a sweat at least five days a week.
● Minimize starchy foods like rice meals.
● Completely avoid sugar, red meat and oily sweets.
● Include plenty of fruits, vegetables and protein in your diet.
These lifestyle changes along with treatment can help prevent liver damage or even reverse liver disease in the early stages. Moreover, early detection and management of grade 1 fatty liver disease can help prevent progression of the disease and preserve liver function.
Defense Strategies:
1. Leafy greens – Nitrates and polyphenols in leafy greens are effective in fighting fatty liver.
2. Legumes- The resistant starch in legumes accelerates blood glucose levels and prevents non-alcoholic liver cirrhosis.
3. Fish – Omega-3 fatty acids in fish are effective in reducing liver fat and lowering triglycerides.
4. High-Fiber Foods- Consuming high-fiber foods prevents fatty liver by lowering triglycerides.
5. Plant seeds – The vitamin-E antioxidant, mainly in sunflower seeds, is effective in fighting non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
6. Garlic- Use of garlic helps in weight loss by reducing fat in people with fatty liver disease.
7. Turmeric- Curcumin, the main ingredient in turmeric, accelerates liver enzymes that are found in elevated levels in people with liver disease.
Factors leading to fatty liver:
Foods that increase blood glucose levels and cause weight gain.
● Alcoholism.
● Sugary drinks, sweets, etc.
● Sweets fried in oil.
● Flour, bakery products containing flour etc.
● Red meat. For example beef, pork etc.
● Consuming too much fruit juice and fruit can cause fructose, the main component of fruit, to accumulate as fat in the liver.
● Rapid weight loss and malnutrition
● Insulin resistance, which impairs the body's ability to respond to the hormone insulin and control blood sugar levels.
Lifestyle changes, such as a nutritious diet and regular exercise, are the best way to lose excess body weight and fat, prevent liver damage, and even reverse liver disease in the early stages.
